The difference between various types of motors
1. Differences between DC and AC motors
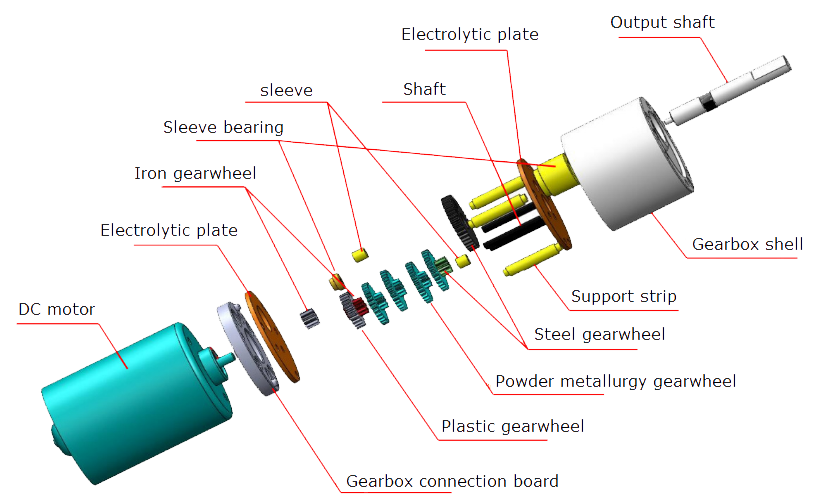
DC motor structure diagram
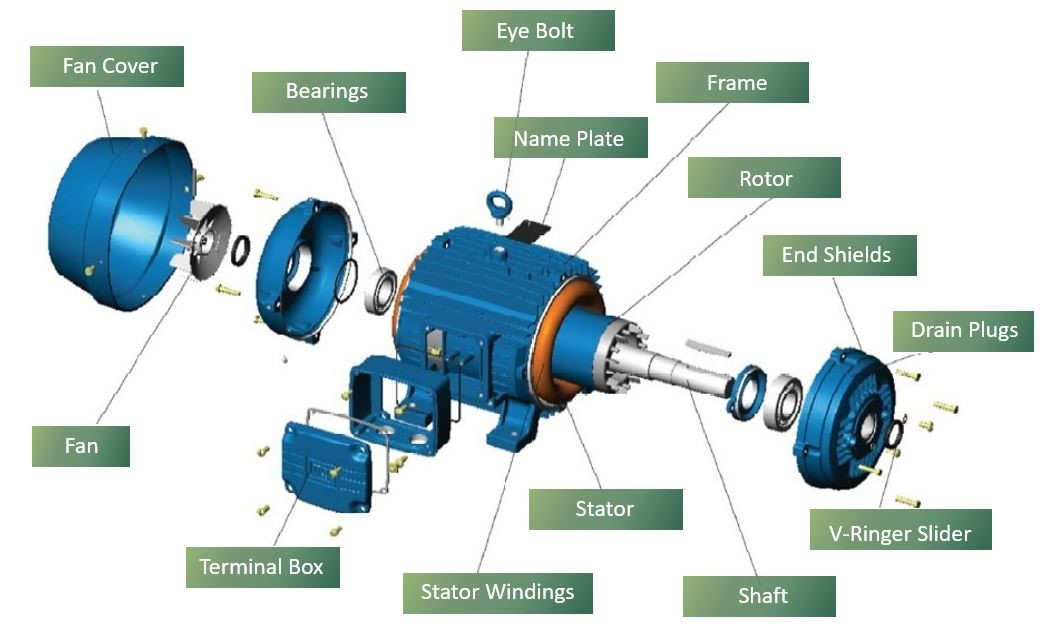
AC motor structure diagram
DC motors use direct current as their power source, while AC motors use alternating current as their power source.
Structurally, the principle of DC motors is relatively simple, but the structure is complex and not easy to maintain. The principle of AC motors is complex but the structure is relatively simple, and it is easier to maintain than DC motors.
In terms of price, DC motors with the same power are higher than AC motors. Including the speed control device, the price of DC is higher than that of AC. Of course, there are also great differences in structure and maintenance.
In terms of performance, because the speed of DC motors is stable and the speed control is precise, which is not achievable by AC motors, DC motors have to be used instead of AC motors under strict speed requirements.
The speed regulation of AC motors is relatively complex, but it is widely used because chemical plants use AC power.
2. Differences between synchronous and asynchronous motors
If the rotor rotates at the same speed as the stator, it is called a synchronous motor. If they are not the same, it is called an asynchronous motor.
3. The difference between ordinary and variable frequency motors
First of all, ordinary motors cannot be used as variable frequency motors. Ordinary motors are designed according to constant frequency and constant voltage, and it is impossible to fully adapt to the requirements of frequency converter speed regulation, so they cannot be used as variable frequency motors.
The impact of frequency converters on motors is mainly on the efficiency and temperature rise of motors.
The frequency converter can generate different degrees of harmonic voltage and current during operation, so that the motor runs under non-sinusoidal voltage and current. The high-order harmonics in it will cause the motor stator copper loss, rotor copper loss, iron loss and additional loss to increase.
The most significant of these is the rotor copper loss. These losses will cause the motor to generate additional heat, reduce efficiency, reduce output power, and the temperature rise of ordinary motors will generally increase by 10%-20%.
The frequency converter carrier frequency ranges from several kilohertz to more than ten kilohertz, which makes the stator winding of the motor withstand a very high voltage rise rate, which is equivalent to applying a very steep impulse voltage to the motor, making the inter-turn insulation of the motor withstand a more severe test.
When ordinary motors are powered by frequency converters, the vibration and noise caused by electromagnetic, mechanical, ventilation and other factors will become more complicated.
The harmonics contained in the variable frequency power supply interfere with the inherent spatial harmonics of the electromagnetic part of the motor, forming various electromagnetic excitation forces, thereby increasing the noise.
Due to the wide operating frequency range of the motor and the large speed variation range, the frequencies of various electromagnetic force waves are difficult to avoid the inherent vibration frequencies of the various structural parts of the motor.
When the power supply frequency is low, the loss caused by the high-order harmonics in the power supply is large; secondly, when the speed of the variable motor is reduced, the cooling air volume decreases in direct proportion to the cube of the speed, resulting in the heat of the motor not being dissipated, the temperature rise increases sharply, and it is difficult to achieve constant torque output.
4. The structural difference between ordinary motors and variable frequency motors
01. Higher insulation level requirements
Generally, the insulation level of variable frequency motors is F or higher. The insulation to the ground and the insulation strength of the wire turns should be strengthened, and the ability of the insulation to withstand impulse voltage should be considered in particular.
02. Higher vibration and noise requirements for variable frequency motors
Variable frequency motors should fully consider the rigidity of the motor components and the whole, and try to increase their natural frequency to avoid resonance with each force wave.
03. Different cooling methods for variable frequency motors
Variable frequency motors generally use forced ventilation cooling, that is, the main motor cooling fan is driven by an independent motor.
04. Different protection measures are required
Bearing insulation measures should be adopted for variable frequency motors with a capacity of more than 160KW. It is mainly easy to produce magnetic circuit asymmetry and shaft current. When the current generated by other high-frequency components is combined, the shaft current will increase greatly, resulting in bearing damage, so insulation measures are generally taken. For constant power variable frequency motors, when the speed exceeds 3000/min, special high-temperature resistant grease should be used to compensate for the temperature increase of the bearing.
05. Different cooling system
The variable frequency motor cooling fan uses an independent power supply to ensure continuous cooling capacity.
2.Basic knowledge of motors
Motor selection
The basic contents required for motor selection are:
The type of load driven, rated power, rated voltage, rated speed, and other conditions.
Load type·DC motor·Asynchronous motor·Synchronous motor
For continuous production machinery with stable load and no special requirements for starting and braking, permanent magnet synchronous motors or ordinary squirrel cage asynchronous motors should be preferred, which are widely used in machinery, water pumps, fans, etc.
For production machinery with frequent starting and braking and requiring large starting and braking torque, such as bridge cranes, mine hoists, air compressors, irreversible rolling mills, etc., permanent magnet synchronous motors or wound asynchronous motors should be used.
For occasions without speed regulation requirements, where constant speed is required or the power factor needs to be improved, permanent magnet synchronous motors should be used, such as medium and large capacity water pumps, air compressors, hoists, mills, etc.
For production machinery that requires a speed regulation range of more than 1:3 and requires continuous, stable and smooth speed regulation, it is advisable to use permanent magnet synchronous motors or separately excited DC motors or squirrel cage asynchronous motors with variable frequency speed regulation, such as large precision machine tools, gantry planers, rolling mills, hoists, etc.
Generally speaking, the motor can be roughly determined by providing the driven load type, rated power, rated voltage, and rated speed of the motor.
However, if the load requirements are to be optimally met, these basic parameters are far from enough.
Other parameters that need to be provided include: frequency, working system, overload requirements, insulation level, protection level, moment of inertia, load resistance torque curve, installation method, ambient temperature, altitude, outdoor requirements, etc. (provided according to specific circumstances)
3.Basic knowledge of motors
Steps for motor selection
When the motor is running or fails, the four methods of looking, listening, smelling and touching can be used to prevent and eliminate the fault in time to ensure the safe operation of the motor.
1. Look
Observe whether there are any abnormalities during the operation of the motor, which are mainly manifested in the following situations.
1. When the stator winding is short-circuited, you may see smoke coming out of the motor.
2. When the motor is seriously overloaded or running in phase loss, the speed will slow down and there will be a heavier “buzzing” sound.
3. When the motor is running normally, but suddenly stops, you will see sparks coming out of the loose connection; the fuse is blown or a part is stuck.
4. If the motor vibrates violently, it may be that the transmission device is stuck or the motor is not fixed well, the foot bolts are loose, etc.
5. If there are discoloration, burn marks and smoke marks on the contact points and connections inside the motor, it means that there may be local overheating, poor contact at the conductor connection or winding burnt, etc.
2. Listen
When the motor is running normally, it should emit a uniform and lighter “buzzing” sound, without noise and special sounds.
If the noise is too loud, including electromagnetic noise, bearing noise, ventilation noise, mechanical friction noise, etc., it may be a precursor or fault phenomenon.
1. For electromagnetic noise, if the motor makes a high, low and heavy sound, the reasons may be as follows:
(1) The air gap between the stator and the rotor is uneven. At this time, the sound is high and low, and the interval between high and low sounds remains unchanged. This is caused by bearing wear, which makes the stator and rotor non-concentric.
(2) The three-phase current is unbalanced. This is caused by the three-phase winding being grounded incorrectly, short-circuited or having poor contact. If the sound is very dull, it means that the motor is seriously overloaded or running in a phase-missing manner.
(3) The iron core is loose. During the operation of the motor, the vibration causes the iron core fixing bolts to loosen, causing the iron core silicon steel sheet to loosen and make noise.
2. For bearing noise, you should monitor it frequently during the operation of the motor. The monitoring method is: put one end of the screwdriver against the bearing installation part and the other end close to your ear, and you can hear the sound of the bearing running. If the bearing operates normally, the sound is a continuous and fine “rustling” sound, without any fluctuations or metal friction sounds.
If the following sounds occur, it is an abnormal phenomenon:
(1) There is a “squeaking” sound when the bearing is running. This is a metal friction sound, which is generally caused by a lack of oil in the bearing. The bearing should be disassembled and an appropriate amount of grease should be added.
(2) If a “chirping” sound occurs, this is the sound made when the ball rotates. It is generally caused by the drying of the grease or lack of oil. An appropriate amount of grease can be added.
(3) If a “clicking” or “squeaking” sound occurs, it is the sound produced by the irregular movement of the ball in the bearing. This is caused by the damage of the ball in the bearing or the long-term non-use of the motor, resulting in the drying of the grease.
3. If the transmission mechanism and the driven mechanism make a continuous sound instead of a fluctuating sound, it can be handled according to the following situations.
(1) Periodic “pop” sound is caused by the uneven belt joint.
(2) Periodic “dong dong” sound is caused by looseness between the coupling or pulley and the shaft, as well as wear of the key or keyway.
(3) Uneven collision sound is caused by the blades colliding with the fan cover.
3. Smell
Failures can also be judged and prevented by smelling the motor.
Open the junction box and smell it to see if there is a burnt smell. If a special paint smell is found, it means that the internal temperature of the motor is too high; if a strong burnt smell or burnt smell is found, it may be that the insulation layer maintenance net is broken or the winding has been burned.
If there is no smell, it is necessary to use a megohmmeter to measure the insulation resistance between the winding and the casing. If it is less than 0.5 megohms, it must be dried. If the resistance is zero, it means that it is damaged.
4. Touch
Touching the temperature of some parts of the motor can also determine the cause of the fault.
To ensure safety, use the back of your hand to touch the motor casing and the surrounding parts of the bearing.
If the temperature is abnormal, the reasons may be as follows:
1. Poor ventilation. Such as fan falling off, ventilation duct blockage, etc.
2. Overload. The current is too large and the stator winding is overheated.
3. The stator winding turns are short-circuited or the three-phase current is unbalanced.
4. Frequent starting or braking.
5. If the temperature around the bearing is too high, it may be caused by bearing damage or lack of oil.
Motor bearing temperature regulations, causes and treatment of abnormalities
The regulations stipulate that the maximum temperature of rolling bearings shall not exceed 95℃, and the maximum temperature of sliding bearings shall not exceed 80℃. And the temperature rise shall not exceed 55℃ (the temperature rise is the bearing temperature minus the ambient temperature during the test).
Causes and treatments for excessive bearing temperature rise:
(1) Cause: The shaft is bent and the center line is not accurate. Treatment: Find the center again.
(2) Cause: The foundation screws are loose. Treatment: Tighten the foundation screws.
(3) Cause: The lubricant is not clean. Treatment: Replace the lubricant.
(4) Cause: The lubricant has been used for too long and has not been replaced. Treatment: Clean the bearings and replace the lubricant.
(5) Cause: The ball or roller in the bearing is damaged. Treatment: Replace the bearing with a new one.
Anhui Mingteng Permanent-Magnetic Machinery & Electrical Equipment Co., Ltd.(https://www.mingtengmotor.com/) has experienced 17 years of rapid development. The company has developed and produced more than 2,000 permanent magnet motors in conventional, variable frequency, explosion-proof, variable frequency explosion-proof, direct drive, and explosion-proof direct drive series. The motors have been successfully operated on fans, water pumps, belt conveyors, ball mills, mixers, crushers, scrapers, oil pumps, spinning machines and other loads in different fields such as mining, steel, and electricity, achieving good energy-saving effects and gaining wide acclaim.
Copyright: This article is a reprint of the original link:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/hLDTgGlnZDcGe2Jm1oX0Hg
This article does not represent our company’s views. If you have different opinions or views, please correct us!
Post time: Nov-01-2024